Folding steps with different bases. The foot has a natural appearance. Designing a task for independent development
In the first statistic we have identified what mononomials are. From which materials we will analyze how to choose the butt that will stink. Here we will look at such actions as the addition, addition, multiplication, division of mononomials and their reduction at the stage with a natural display. We will show how such operations are defined, and the basic rules of their interpretation and those that may result. All theoretical positions, as always, will be illustrated with examples along with descriptions of solutions.
It is best to use the standard notation of monomials, so all the expressions that will appear in the statistics are indicated in the standard view. If the tasks are different from the beginning, it is recommended to bring them to their original form from the beginning.
Rules for the addition and expansion of monomials
The simplest operations that can be carried out with monomials are the most obvious addition. In this case, the result of this action will be a polynomial (a monomial in the same case).
When we add or remove monomials, we first write down in formal form the total sum and the difference, after which we will simply say that it is the highest. As there are similar additions, they need to be aligned and the arms need to be opened. Let's explain with an example.
Butt 1
Umova: Construct the folding of monomials − 3 · x and 2, 72 · x 3 · y 5 · z.
Decision
Let's write down the amount of output. Add the arms and put a plus between them. We have this:
(− 3 x) + (2, 72 x 3 y 5 z)
If we open the arms, we will see - 3 x + 2, 72 x 3 y 5 z. This is a rich term of notation in the standard form, which will be the result of the addition of these monomials.
Subject:(− 3 x) + (2.72 x 3 y 5 z) = − 3 x + 2.72 x 3 y 5 z.
Since we are given three, even more additions, we do the same thing.
Butt 2
Umova: carry out the assignments with rich members in the correct order
3 a 2 - (- 4 a c) + a 2 - 7 a 2 + 4 9 - 2 2 3 a c
Decision
Let’s finish opening the arms.
3 a 2 + 4 a c + a 2 - 7 a 2 + 4 9 - 2 2 3 a c
Mi bachimo, scho otramanii viraz can be forgiven by the way of bringing such dodanki:
3 a 2 + 4 a c + a 2 - 7 a 2 + 4 9 - 2 2 3 a c = = (3 a 2 + a 2 - 7 a 2) + 4 a c - 2 2 3 a c + 4 9 = = - 3 a 2 + 1 1 3 a c + 4 9
We have the richest member, which will be the result of this action.
Subject: 3 a 2 - (- 4 a c) + a 2 - 7 a 2 + 4 9 - 2 2 3 a c = - 3 a 2 + 1 1 3 a c + 4 9
In principle, we can add and subtract two monomials with certain interchanges so as to eliminate the monomial as a result. For this purpose, it is necessary to reach the minds of many people who are intermingling with each other and the members of the same group are emerging. About those who are afraid, we understand in the okremіy statistics.
Rules for multiplying monomials
This multiplying action does not impose any restrictions on the multipliers. Monomials that multiply do not have to be combined with every additional mind so that the result is a monomial.
To eliminate the multiplicity of monomials, you need to enter the following terms:
- Write your tweet correctly.
- Open the arms in a straight line.
- Group the multipliers according to the possibility with the new ones and the numerical multipliers together.
- Vikonati necessary actions with numbers and stand up to the multipliers that have lost, the power of multiple stages with the same basics.
I wonder how it works in practice.
Butt 3
Umova: Multiply the monomials 2 x 4 y z i - 7 16 t 2 x 2 z 11.
Decision
Let’s finish the creation.
The arches are curved in a new way and are removed from the foot:
2 x 4 y z - 7 16 t 2 x 2 z 11
2 - 7 16 t 2 x 4 x 2 y z 3 z 11
All that we have lost to earn is to multiply the numbers in the first arms and establish the power of the steps for others. The result is as follows:
2 - 7 16 t 2 x 4 x 2 y z 3 z 11 = - 7 8 t 2 x 4 + 2 y z 3 + 11 = = - 7 8 t 2 x 6 y z 14
Subject: 2 x 4 y z - 7 16 t 2 x 2 z 11 = - 7 8 t 2 x 6 y z 14 .
Since in our minds there are three rich elements and more, we multiply them behind this very algorithm. We will look at the report on the multiplication of mononomial terms in the context of the material.
Rules for raising a monomial to a degree
We know that the natural indicator is the income of a certain number of new multipliers. Their quantity is indicated by the number on the display. According to this value, raising a monomial to a step is equal to the multiplication of the indicated number of new monomials. I'm amazed at how stubborn I am.
Butt 4
Umova: Add the monomial − 2 · a · b 4 to step 3.
Decision
We can replace the multiplication of the step by multiplying 3 monomials − 2 · a · b 4 . Let's write down and read out the following:
(−2 · a · b 4) 3 = (−2 · a · b 4) · (−2 · a · b 4) · (−2 · a · b 4) = = ((−2) · (− 2) · (−2)) · (a · a · a) · (b 4 · b 4 · b 4) = − 8 · a 3 · b 12
Subject:(− 2 · a · b 4) 3 = − 8 · a 3 · b 12 .
But what about that situation, if rhubarb makes a great show? It is difficult to write down the great number of multiplicities. Therefore, in order to achieve such a task, we need to build up the power of the stage, and the power of the stage itself will increase and the power of the stage at the stage.
Virishimo the treasure, as we have brought the place, in the manner indicated.
Butt 5
Umova: Add the number − 2 · a · b 4 to the third step.
Decision
Knowing the power of the stage, we can move to the next level:
(−2 · a · b 4) 3 = (−2) 3 · a 3 · (b 4) 3 .
After which we reduce it to stage - 2 and the stagnation of power stage:
(−2) 3 · (a) 3 · (b 4) 3 = − 8 · a 3 · b 4 · 3 = − 8 · a 3 · b 12 .
Subject:− 2 · a · b 4 = − 8 · a 3 · b 12 .
The creation of the monomial in the world was also dedicated to the article.
Rules for sub-monomials
The rest of the work with monomials, which we will look at in this material, is to divide the monomials into monomials. As a result, we are obliged to reject the rational (algebraic) argument (in some cases it is possible to retain a monomial). Let us immediately clarify that the division on the zero monomial is not calculated, since the division on 0 is not indicated.
To complete this section, we need to write down the meaning of the monomial in the form of a fraction and its abbreviation, which is so possible.
Butt 6
Umova: Convert the subsection of the monomial − 9 · x 4 · y 3 · z 7 to − 6 · p 3 · t 5 · x 2 · y 2 .
Decision
Let's understand how to write monomials in the form of a fraction.
9 x 4 y 3 z 7 - 6 p 3 t 5 x 2 y 2
This conversation can be short. After you select this information, it can be deleted:
3 x 2 y z 7 2 p 3 t 5
Subject:- 9 x 4 y 3 z 7 - 6 p 3 t 5 x 2 y 2 = 3 x 2 y z 7 2 p 3 t 5 .
The minds for which, as a result of the division of mononomials, we are removing a mononomial, are brought into line with the statistics.
If you have marked a favor in the text, please see it and press Ctrl+Enter
If you don’t call it the eighth step, what are we doing here? We are planning a program for 7th grade. Oh boy, did you guess? This is the formula for short multiplication, and itself is the difference in squares! Ignorable:
We respectfully marvel at the banner. It’s already similar to one of the numbers in the numbers department, but what’s wrong? The order of the dodanks is not the same. If they were to be remembered in some places, it would be possible to establish a rule.
Ale yak tse zrobiti? It appears even easier: here we are helped by the guy’s step of the flag bearer.
With a magical rite, the Dodanki changed places. This “appearance” is stagnant for any kind of view as a paired world: we can without fail change the signs in the arms.
Ale important to remember: all signs change overnight!
Let's turn around, for example:
I know the formula:
Tsilimi We call natural numbers that are adjacent to them (then we know them with the sign “”) and the number.
a whole positive number, and nothing differs from the natural one, everything looks exactly like the front section.
And now let's look at new developments. Let’s finish with the show, which is more ancient.
Whether the number is in the zero degree of the ancient unit:
As before, we ask ourselves: why is this so?
Let's take a look at the basic step. Let's take, for example, multiply by:
Then, we multiplied the number by, and subtracted those that were - . How much do you need to multiply so that nothing changes? That's right, on. To mean.
We can earn the same with a sufficient number:
Let's repeat the rule:
Whether there is a number in the zero level there are ancient ones.
There are a lot of rules and blame. And here there is the same number (as the basis).
On the one hand, whatever the world is guilty of, no matter how much you multiply zero by itself, you still subtract zero, that’s clear. On the other hand, as well as the number in the zero level, it can be comparable. What's the truth? Mathematicians decided not to communicate and decided to add zero to the zero level. So now we can’t not only divide by zero, but also raise it to the zero level.
Let's go away. Besides natural numbers and numbers, there are also negative numbers. To understand what a negative step is, let’s do it like last time: multiplying a normal number with an equally negative one:
It’s already difficult for Zvidsi to say:
Now we have expanded the rule to a higher level:
Well, let’s formulate a rule:
A number with a negative world back to the same number is positive. Ale pri tsomu the basis cannot be null:(It is not possible to divide).
Let's summarize the pouches:
I. Viraz is not indicated at the time. Something like that.
II. Whether there is a number in the zero degree there are ancient units: .
III. A number that is not equal to zero is moved negatively back to the same number in the positive degree: .
Instructions for independent virtuousness:
Well, as always, apply for independent achievement:
Selecting a task for independent solving:
I know, I know, the numbers are scary, but we still need to prepare for everything! Check these applications and sort out their solutions if you can’t figure them out and you’ll learn how to easily deal with them in practice!
It is possible to expand the number of numbers, “additional” ones, as an indication of the level.
Now let's take a look rational numbers. What numbers are called rational?
Proof: everything that can be presented is a fraction, a whole number, and a whole number.
To understand what it is "dirty step", let's take a look:
We are aware of offending parts of the equation up to the level:
Now let's guess the rule about "step step":
How do you need to reduce the number to a step in order to remove it?
This formula is a derivative of the root step.
I’ll guess: the root of the th degree of a number () is the number that, when raised to a level, is higher.
So, the root step is the operation that leads to the return to the step: .
Come out now. Of course, this extension can be expanded: .
Now let’s add the number cruncher: what is it? The answer is easy to follow by following the “step by step” rule:
How can we substitute whatever number? Even the root can be removed from all numbers.
Zhodne!
We can guess the rule: if it is a number, if the next step is added, the number is more positive. So it is not possible to extract the root of a paired step from negative numbers!
And this means that it is not possible to put such numbers into a fractional level with a double sign, so that the result is not meaningful.
What about vislovlyuvannya?
But here there is a problem.
The number can be represented in the form of other, rapid fractions, for example, or.
And it turns out that it is true, but it is not true, or even just two different entries of the same number.
Or another way: once, then you can write it down. But let us write down the indicator in a different way, and the inadmissibility is again rejected: (then we would have rejected a completely different result!).
To avoid such paradoxes, we consider Only a positive base step with a shotgun display.
Ozhe, yakscho:
- - natural number;
- - whole number;
Apply:
The steps with a rational indicator are even shorter for the transformation of viruses from roots, for example:
5 butts for training
Collection of 5 butts for training
1. Don’t forget about the primary power of the steps:
2. . Here we guess that you forgot to read the table of steps:
aje - tse chi. The decision changes automatically: .
Well, now it’s more complicated. We'll figure it out right now step with irrational display.
All the rules and powers of the levels here are the same as for the level with a rational display, behind the scenes
And after all, irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be seen as a fraction, and also whole numbers (and irrational numbers are all real numbers, except rational ones).
When we combined the steps with natural, purposeful and rational manifestations, we immediately formed some kind of “image”, “analogy”, or a description of more basic terms.
For example, a step with a natural indicator is the same number multiplied by itself;
...number in the zero stage- no number, multiplied by itself once, then they have not yet begun to multiply it, which means that the number itself has not yet appeared - the result is not only the “preparing of the number”, but the number itself;
...step from a whole negative display- What happened here was some kind of “return process”, so that the number was not multiplied by itself, but divided.
Among other things, science often has a stage with a complex indicator, but the indicator is not a valid number.
Although at school we don’t think about such complexities, but you will be able to grasp these new concepts at the institute.
WHERE YOU WILL GO! (once you learn how to use such butts:))
For example:
Virish independently:
Analysis of solutions:
1. Let’s take a look at the basic rule for adding step to step:
Now marvel at the display. Doesn’t that remind you of anything? Let's guess the formula for short multiplication of squares:
In this situation,
Log in:
Subject: .
2. We bring the fractions at the indicators of the steps to the same form: either offensive tens, or offensively equal. Let's ignore, for example:
Submission: 16
3. Nothing special, stagnation of the initial power of the steps:
PUSHED RUBBISH
Secondary level
The step is called viraz in mind: , de:
- — base step;
- - stage display.
Step with natural display (n = 1, 2, 3,...)
Raising a number to the natural notch n means multiplying the number by itself:
Step from whole indicator (0, ±1, ±2,...)
As an indication of stage є not at all positive number:
Zvedennia at the zero step:
Wislav of non-significances, because, on one side, be the world - tse, on the other - be the number - the world - tse.
As an indication of stage є not at all negative number:
(It is not possible to divide).
Once again about zeros: there are no meanings at all. Something like that.
Apply:
Step from rational display
- - natural number;
- - whole number;
Apply:
Power of steps
To make things simpler, let’s try to understand: did the intelligence agencies come to the authorities? Let's bring it up.
I wonder: what is that?
For appointments:
Well, the right side of this line comes out with the following statement:
Ale behind the indicated steps of the number with the indicator, then:
What needed to be brought up.
butt : Forgive Viraz
Decision : .
butt : Forgive Viraz
Decision : It is important to note that our rules obov'yazkovo However, they may be substituted. Therefore, the step from the base will be subtracted, but will be deprived of the multiplier:
Another important thing is respect: this rule is only for adding steps!
Every time you can’t write what.
So, just like from the previous power, we are advancing to the next step:
We regroup this solid like this:
It turns out that the expression multiplies on itself once, then, based on the meanings, this is the stage of the number:
In fact, this can be called “a show-off for the temples.” Ale nіkoli nіkoli nіkolo nіzhání kogo robít sumí: !
Let’s guess the formulas for short multiplication: how many times have we wanted to write? Ale tse not so, aje.
Stage from a negative basis.
Until that moment we discussed only those who may display step. What kind of setup is there? At the steps natural showman foundation can be used whatever the number .
And in fact, we can even multiply one by one any number, be it positive, negative, or even negative. Let's think about what signs (" or " ") represent the level of positive and negative numbers?
For example, will a number be positive or negative? A? ?
From the first, everything became clear: no matter how many positive numbers we multiplied by one, the result would be positive.
Ale with negative little bits is better. We remember the simple rule from 6th grade: “minus by minus gives a plus.” Tobto, or. Ale yakscho mi multiply (), viide - .
And so infinitely: with a cutaneous attack, the multiple sign changes. You can formulate these simple rules:
- guy step - number more positive.
- Negative number added to unpaired step - number more negative.
- The positive number of whatever world is - the number is more positive.
- Zero, whatever the world, is like zero.
Therefore, independently, what kind of sign will be such expressions:
| 1. | 2. | 3. |
| 4. | 5. | 6. |
Did it fit? Axis:
1) ; 2) ; 3) ; 4) ; 5) ; 6) .
The first few butts, I hope, have everything cleared up? We simply marvel at the basis of that level of display, and it is a stagnant rule.
In the case of 5) everything is not as scary as it sounds: it doesn’t even matter what the level is, which means the result will always be positive. Well, let’s just say, if the basis is equal to zero. Is the base not equal? Obviously not, that's why.
Butt 6) is no longer so simple. Here you need to know what is less: what? If you guess what, it becomes clear that, of course, the difference is less than zero. Then rule 2 remains: the result will be negative.
І again, vikorista’s most important step:
Everything as before - we write down the assigned steps and divide them one by one, divide them into bets and remove them:
The first step is to remove the remaining rule by releasing a number of butts.
Calculate the values of viruses:
Decision :
If you don’t call it the eighth step, what are we doing here? We are planning a program for 7th grade. Oh boy, did you guess? This is the formula for short multiplication, and itself is the difference in squares!
Ignorable:
We respectfully marvel at the banner. It’s already similar to one of the numbers in the numbers department, but what’s wrong? The order of the dodanks is not the same. If they were to be remembered in some places, it would be possible to establish rule 3. How to make money? It appears even easier: here we are helped by the guy’s step of the flag bearer.
If you multiply this by, nothing will change, what’s wrong? Ale now comes out like this:
With a magical rite, the Dodanki changed places. This “appearance” is stagnant for any kind of view as a paired world: we can without fail change the signs in the arms. Ale important to remember: All signs change overnight! It is impossible to replace, having changed only one minus that we dislike!
Let's turn around, for example:
I know the formula:
Well, now the remaining rule is:
How is it communicated? Firstly, as before: the concept of the stage is revealed and simply:
Well, now let’s open the arms. How many letters are there? once in multiples - what can you guess? Nothing more than a significant operation multiplication: of everything there appeared multiples of Tobto, behind the figures, a step of numbers with a display:
Butt:
Step with irrational display
In addition to information about the steps for the middle level, let’s look at the step with the irrational indicator. All the rules and power of the steps here are exactly the same as for the step with a rational display, behind the scenes - and even for the significant irrational numbers - the numbers, as it is impossible to see the fraction in sight, and the whole numbers (then the irra central numbers - all actions numbers, besides rational ones).
When we combined the steps with natural, purposeful and rational manifestations, we immediately formed some kind of “image”, “analogy”, or a description of more basic terms. For example, a step with a natural indicator is the same number multiplied by itself; a number in the zero degree is a number multiplied by itself once, so that they have not yet begun to multiply it, which means that the number itself has not yet appeared - the result is not only the “preparing of the number”, but the number itself; This step is a completely negative indicator - the value of any kind of “turnaround process” is that the number is not multiplied by itself, but divided.
It is very difficult to identify the level with an irrational display (in the same way as it is difficult to recognize the 4-dimensional expanse). This is a purely mathematical object that mathematicians created in order to expand the concept level to the entire range of numbers.
Among other things, science often has a stage with a complex indicator, but the indicator is not a valid number. Although at school we don’t think about such complexities, but you will be able to grasp these new concepts at the institute.
So, what are we afraid of, since most irrational display is a step? With all our strength we try to wake you up! :)
For example:
Virish independently:
| 1) | 2) | 3) |
Types:
- Let's guess the formula for the difference of squares. Subject: .
- Let us bring the fractions to their new form: either the offense is tens or the offense is extreme. We reject, for example: .
- Nothing special, the initial power of the steps is stagnant:
SHORT VIKLAD ABOUT THE BASIC FORMULAS
step by step is called viraz viz: , de:
Step from the whole display
step, the indicator of which is a natural number (that is whole and positive).
Step from rational display
step, an indicator of some kind - negative and fractional numbers.
Step with irrational display
step, the indicator of which is an endless tenth of a fraction or a root.
Power of steps
Features of the steps.
- Negative number added to guy step - number more positive.
- Negative number added to unpaired step - number more negative.
- The positive number of whatever world is - the number is more positive.
- Zero be whatever the world is before.
- Whether the number in the zero level is older.
NOW YOU HAVE THE OVER...
How are you doing? Write below in the comments if you deserve anything.
Tell us about your testimony against the rise of the powers of the levels.
Perhaps, you have food. Or propositions.
Write comments.
And good luck on your tests!
How to multiply the stage? Which steps can be multiplied, and which ones cannot? How to multiply a number by a step?
In algebra, you can find out the additional steps in two ways:
1) since the steps are supported by supports;
2) as the stage is looming, however, the demonstrators.
With multiple steps with the same foundations, it is necessary to strip the foundation to excess, and the displays - to fold:
With multiple steps with new displays, the back display can be carried by the arms:
Let's look at how to multiply the steps on specific butts.
Do not write one step at a time, but if there are multiple steps, write:
With a multiplying number of steps it can be different. Just remember that you don’t have to write the multiplication sign before the letter:
In virazas, the signs at the steps end up in front of us.
If you need to multiply a number by a step, first reduce it to a step, and then multiply:
www.algebraclass.ru
Adding, subtracting, multiplying and sub-steps
Folding and removing steps
Obviously, numbers in steps can be added up like other quantities the path of their folded one after one with their signs.
So, the sum a 3 and b 2 є a 3 + b 2.
Sum a 3 - b n i h 5 -d 4 є a 3 - b n + h 5 - d 4.
Coefficients the same steps, the same changes may fold or rise.
So, the sum 2a 2 and 3a 2 is equal to 5a 2.
It is also obvious that you can take two squares a, or three squares a, or five squares a.
Ale step various changesі different stages however, the most important, it is their fault to fold their folds with their own signs.
So, the sum of a 2 and a 3 is the sum of a 2 + a 3.
It is obvious that the square of the number a, and the cube of the number a, are not equal to the second square of a, but rather to the second cube of a.
Sum a 3 b n і 3a 5 b 6 є a 3 b n + 3a 5 b 6 .
Vіdnіmannya The steps are carried out in the same order as they were added, except that the signs appear due to the changes.
Abo:
2a 4 - (-6a 4) = 8a 4
3h 2 b 6 - 4h 2 b 6 = -h 2 b 6
5(a - h) 6 - 2(a - h) 6 = 3(a - h) 6
More steps
Numbers in steps can be multiplied, as well as other quantities, written one after another, with or without the multiplication sign.
Thus, the result of multiplying a3 by b2 is equivalent to a3b2 or aaabb.
Abo:
x -3 ⋅ a m = a m x -3
3a 6 y 2 ⋅ (-2x) = -6a 6 xy 2
a 2 b 3 y 2 ⋅ a 3 b 2 y = a 2 b 3 y 2 a 3 b 2 y
The result in the rest of the application may be the ordering of the folding paths of the new ones.
Viraz will now see: a 5 b 5 y 3 .
An equal number of numbers (changeable) in steps, we can add up, so that if two of them are multiplied, then the result is the same number (changeable) in steps, which is the same sumi steps of dodanki.
So, a 2 .a 3 = aa.aaa = aaaaa = a 5 .
Here 5 is the same step in the result of multiplication, which is equal to 2 + 3, the sum of the steps of additions.
So, a n a m = a m + n.
For a n a is taken as a multiplier as many times as there is a level n;
І a m is taken as a multiplier as many times as the level of m;
Tom, A step with the same basics can be multiplied by the way of folding the display steps.
So, a 2 .a 6 = a 2+6 = a 8 . x 3 .x 2 .x = x 3+2+1 = x 6 .
Abo:
4a n ⋅ 2a n = 8a 2n
b 2 y 3 ⋅ b 4 y = b 6 y 4
(b + h - y) n ⋅ (b + h - y) = (b + h - y) n+1
Multiply (x 3 + x 2 y + xy 2 + y 3) ⋅ (x - y).
Version: x 4 - y 4.
Multiply (x 3 + x - 5) ⋅ (2x 3 + x + 1).
This rule is also true for numbers that show any level negative.
1. So, a-2.a-3 = a-5. This can be written down in the form (1/aa). (1/aaa) = 1/aaaaa.
2. y-n. y-m = y-n-m.
3. a -n. am = am-n.
When a + b is multiplied by a - b, the result is the same as a 2 - b 2: then
The result of multiplying the sum and difference of two numbers is equal to the sum and difference of their squares.
How does the sum and difference of two numbers multiply? square, the result is similar to the sum or the difference between these numbers in fourth step.
So, (a - y). (a + y) = a 2 - y 2.
(a 2 - y 2)⋅(a 2 + y 2) = a 4 - y 4.
(a 4 - y 4)⋅(a 4 + y 4) = a 8 - y 8.
Division of steps
Numbers in steps can be divided, like other numbers, selected from each other, or placed in the form of a fraction.
In this way a 3 b 2 divisions into b 2, adding a 3.
Writing a 5 divided by a 3 looks like $\frac $. Ale tse one a 2. A number of numbers
a +4 , a +3 , a +2 , a +1 , a 0 , a -1 , a -2 , a -3 , a -4 .
Either number can be divided by another, and the indicator is more expensive differences displays of divisions of numbers.
When the steps are divided from the same base, their indicators appear..
So, y3: y2 = y3-2 = y1. Tobto $\frac = y$.
I a n+1:a = n+1-1 = a n. Tobto $frac = a^n$.
Abo:
y 2m: y m = y m
8a n+m: 4a m = 2a n
12(b + y) n: 3(b + y) 3 = 4(b + y) n-3
The rule is also true for numbers s negative the values of the steps.
The result is subdivided from a-5 to a-3, compared to a-2.
Also, $\frac: \frac = \frac .\frac = \frac = \frac $.
h 2:h -1 = h 2+1 = h 3 or $h^2:\frac = h^2.\frac = h^3$
It is necessary to thoroughly master the multiplication and sub-steps, as such operations will become widely used in algebra.
Butts tying the butts with fractions to place the numbers in steps
1. Change the display of steps in $\frac$ Type: $\frac$.
2. Change the display of steps at $\frac$. Subject: $\frac$ or 2x.
3. Change the indicators of steps a 2 /a 3 and a -3 /a -4 and bring them to the final sign.
a 2 .a -4 є a -2 is the first number.
a 3 .a -3 є a 0 = 1, another number.
a 3 .a -4 є a -1 back-of-the-envelope number book.
After all, a -2 /a -1 and 1/a -1 .
4. Change the indicators of steps 2a 4 /5a 3 and 2 /a 4 and bring them to the final sign.
Version: 2a 3 /5a 7 and 5a 5 /5a 7 or 2a 3 /5a 2 and 5/5a 2.
5. Multiply (a 3 + b)/b 4 (a - b)/3.
6. Multiply (a 5 + 1)/x 2 (b 2 - 1)/(x + a).
7. Multiply b4/a-2 by h-3/x and an/y-3.
8. Divide a4/y3 into a3/y2. Submit: a/y.
Power stage
We can guess what we will understand in this lesson power levels with natural indicators and zero. The levels of rationality and their power will be discussed in lessons for 8th grade.
The step with a natural display is a number of important authorities who allow you to feel the calculations in the butts with the steps.
Power #1
Additional steps
With multiple steps with the same bases, the base is lost without changes, and the indicators of the steps are added up.
a m · a n = a m + n, where “a” is a number, and “m”, “n” is a natural number.
This power of steps is the same as that of three or more steps.
b b 2 b 3 b 4 b 5 = b 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = b 15
6 15 36 = 6 15 6 2 = 6 15 6 2 = 6 17
(0.8) 3 · (0.8) 12 = (0.8) 3 + 12 = (0.8) 15
Let us remember that the appointed authorities had to go through many steps with new bases. It’s impossible to get close to their folding.
It is not possible to replace the sum (3 3 + 3 2) with 3 5. This is understandable, because
porahuvati (3 3 + 3 2) = (27 + 9) = 36, and 3 5 = 243
Authority No. 2
Private steps
When dividing the steps with the same bases, the base is removed without changes, and from the indicator of the divided step, the indicator of the sharer’s step is raised.
(2b) 5: (2b) 3 = (2b) 5 − 3 = (2b) 2
11 3 − 2 4 2 − 1 = 11 4 = 44
butt. Virishity equal. Vikorist is the power of the private stage.
3 8: t = 3 4
Version: t = 3 4 = 81
Corying with authorities No. 1 and No. 2, you can easily sense the inversion and carry out calculations.
- butt. Forgive Viraz.
4 5m + 6 4 m + 2: 4 4m + 3 = 4 5m + 6 + m + 2: 4 4m + 3 = 4 6m + 8 − 4m − 3 = 4 2m + 5
butt. Know the significance of the viraza, the vikorist and power level.
2 11 − 5 = 2 6 = 64
It is worth remembering that the authorities 2 only had about half the steps with the same basics.
You cannot replace the difference (4 3 −4 2) with 4 1. This is reasonable, because you can calculate (4 3 −4 2) = (64 − 16) = 48, and 4 1 = 4
Power #3
Step by step
When a step is advanced, the step is removed without change, and the step indicators are multiplied.
(a n) m = a n · m, where “a” is a number, and “m”, “n” are natural numbers.

Restore respect to the power of No. 4, as well as other levels of power, to stand in the turning order.
(a n b n) = (a b) n
So, in order to multiply the steps with new indicators, you can multiply the bases, and leave the stage indicator unchanged.
2 4 5 4 = (2 5) 4 = 10 4 = 10,000
0.5 16 2 16 = (0.5 2) 16 = 1
In larger folding butts, drops may occur if there is an increase in the need to work on the steps with different bases and different displays. In this case, it’s best to do it this way.
For example, 4 5 3 2 = 4 3 4 2 3 2 = 4 3 (4 3) 2 = 64 12 2 = 64 144 = 9216
The butt is cranked at the steps of a tenth shot.
4 21 (−0.25) 20 = 4 4 20 (−0.25) 20 = 4 (4 (−0.25)) 20 = 4 (−1) 20 = 4 1 = 4
Power 5
Private level (fractions)
To display privacy in a stage, you can display several divisions and a sharer in this stage, and divide the first result into another.
(a: b) n = a n: b n, where “a”, “b” are rational numbers, b ≠ 0, n is a natural number.
(5: 3) 12 = 5 12: 3 12
We guess that you can give a fraction in private. Therefore, on the topic of reducing the fraction to steps, we begin the report on the next page.
Steps and roots
Operations in stages and roots. Step from negative ,
zero and shot showman. About language, which is not to make sense.
Operations in stages.
1. With multiple steps with the same basis, their performance develops:
a m · a n = a m + n.
2. When the stages are divided with the same basis, their displays rise up .

3. The stage of the addition of two or many synthetic agents is the same as the addition of stages of these synthetic agents.
4. The stage of correlation (fractions) is the same as the stages of the dividend (numerator) and the dividend (signifier):
(a/b) n = a n / b n.
5. When a step is increased to a step, their indicators are multiplied:
All formulas can be read and completed in both directions, right and wrong.
EXAMPLE (2 3 5 / 15)² = 2² · 3² · 5² / 15² = 900 / 225 = 4 .
Operations with roots. In all formulas hovered below, the symbol means arithmetic root(underneath it is positive).
1. Roots from the creation of many sprouts:
2. The root of the ancient relationship of the roots of the divisible and the shareholder:
![]()
3. When the root is taken to a step, it is enough to take it to that step radical number:

4. If you increase the degree of the root m times and simultaneously enter the number in m - the degree of the root, then the value of the root does not change:
![]()
5. If you change the degree of the root m times and simultaneously subtract the root of the mth degree from the radical number, then the value of the root will not change:
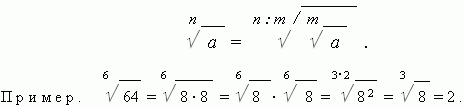
Expanded understanding of the stage. We have already seen the steps with a natural display; All these steps and roots can also be brought up to negative, nullі shot show-offs. All these indicators of steps will require additional designation.
Step with negative display. The level of a given number with a negative (target) indicator is calculated as one, divided by the level of the same number with an indicator, which is equal to the absolute value of the negative indicator:
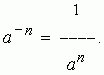
Now the formula a m : a n = a m - n you can use vikoristan not only for m more, lower n, but and at m smaller, lower n .
EXAMPLE a 4: a 7 = a 4 — 7 = a — 3 .
Whatever you want, what is the formula? a m : a n = a m — n bula fair for m = n, we need a different zero stage.
Step with zero indicator. The degree of any non-zero number with a zero exponent is equal to 1.
Accept it. 2 0 = 1, ( – 5) 0 = 1, (– 3 / 5) 0 = 1.
A step with a shotgun display. In order to convert the active number a to the m/n step, you need to subtract the root of the nth step from the mth step of the nth number a:
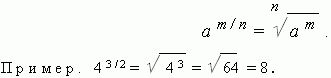
About language, which is not to make sense. There are a bunch of such viruses.
de a ≠ 0 , I can't sleep.
To be fair, let’s assume that x- the day is the number, then it is consistent with the corresponding operation under the heading: a = 0· x, Tobto. a= 0, so let’s think about it: a ≠ 0
— whatever the number.
In truth, let us assume that this is older than this number x, then from the designated operations we can obtain: 0 = 0 · x. But jealousy takes its place when whatever number x, what needed to be accomplished.
0 0 — whatever the number.
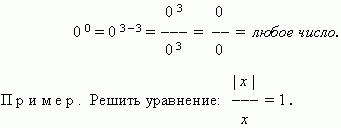
Rozv'yazannya. Let's look at three main types:
1) x = 0 – This value does not satisfy this relative
2) when x> 0 can be removed: x/x= 1, then. 1 = 1, stars next,
what x- Whatever the number; ale beruchi to respect, scho in
to our VIP x> 0, confirm є x > 0 ;
Rules for multiplying steps with different bases
STAGE WITH RATIONAL INDICATOR,
STYLE FUNCTION IV
§ 69. Multiplying and sub-steps with new substructures
Theorem 1. In order to multiply the step with the new bases, it is sufficient to show the steps of the structure, and deprive the base itself, so that
Finished. Behind the steps
2 2 2 3 = 2 5 = 32; (-3) (-3) 3 = (-3) 4 = 81.
We looked at two steps. The truth is that the power is correct for any number of steps with the same bases.
Theorem 2. To separate the step from the same stands, if the indicator of the divisible is larger than the indicator of the sharer, it is enough to raise the indicator of the sharer from the indicator of the divider, and remove the excess from the stand, so that at t > p
(a =/= 0)
Finished. It seems that the division of one number by another is often called a number, which when multiplied by a dilator gives a division. So bring the formula, de a =/= 0, it’s all the same, so let’s complete the formula
Yakshcho t > p , then the number t - p be natural; Well, behind Theorem 1
Theorem 2 has been proven.
Please understand the formula
we have brought to the notice that t > p . Because of what has been achieved so far, it is not possible to work, for example, such concepts:
![]()
Until then, we have not yet seen the level of negative indicators and we do not yet know what kind of sensation can be given to the virus. - 2 .
Theorem 3. To distinguish one step from another, it is enough to multiply the indicators, depriving the base of excess, then
Finished. Vikorist’s important step and theorem of the 1st paragraph can be removed:

what needed to be accomplished.
For example, (2 3) 2 = 2 6 = 64;
![]()
518 (Usno) Significance X from Rivnyan:
1) 2 2 2 2 3 2 4 2 5 2 6 = 2 x ; 3) 4 2 4 4 4 6 4 8 4 10 = 2 x ;
2) 3 3 3 3 5 3 7 3 9 = 3 x ; 4) 1 / 5 1 / 25 1 / 125 1 / 625 = 1 / 5 x .
519. (Ust no.) Forgive:

520. (Ust no.) Forgive:
521. Data on the types of taxes in the form of steps with new steps:
1) 32 and 64; 3) 8 5 and 16 3; 5) 4100 and 3250;
2) -1000 and 100; 4) -27 and -243; 6) 81 75 8 200 and 3 600 4 150.
If you need to know a specific number per step, you can quickly. And now we report back to power levels.
Exponential numbers They reveal great possibilities, they allow us to multiply by adding, and add more easily, without multiplying.
For example, we need to multiply 16 by 64. The multiplication of these two numbers equals 1024. 16 is equal to 4x4, and 64 is equal to 4x4x4. Then 16 by 64 = 4x4x4x4x4, which is also more expensive than 1024.
The number 16 can also look like 2x2x2x2, and 64 can look like 2x2x2x2x2x2, and when multiplied, we subtract 1024 again.
And now the vikory rule. 16=4 2, chi 2 4, 64=4 3, chi 2 6, before that hour 1024=6 4 =4 5, chi 2 10.
Well, our task can be written differently: 4 2 x4 3 =4 5 or 2 4 x2 6 =2 10 and we immediately subtract 1024.
We can create a number of similar applications and, most importantly, multiply the numbers in stages and reduce them to folding display steps, or the exhibitor, understandably, for the minds that they substituted rivals.
Well, we can, without hesitation, say right away that 2 4 x2 2 x2 14 =2 20.
This rule is also true when the numbers are divided into steps, but in this case The dilator component is derived from the dividing exponent. Well, 2 5:2 3 =2 2, which in prime numbers is equivalent to 32:8 = 4, then 2 2. Let's summarize the pouches:
a m x a n = a m+n, a m: a n = a m-n where m i n are whole numbers.
From the first glance you might wonder why multiplication and division of numbers in steps It’s not very easy, even if you first need to figure out the number in exponential form. It doesn’t matter if you see the numbers 8 and 16 in this form, or 23 and 24, but how can you work out the numbers 7 and 17? Or how to deal with these situations, if the number can be presented in exponential form, but the representation of exponential forms of numbers varies greatly. For example, 8 × 9 is equal to 2 3 x 3 2 and in this case we cannot count the exponential. Neither 2 5 nor 3 5 is a answer, and the answer also does not lie in the interval between these two numbers.
So why are you interested in fiddling with this method? Stand without reproach. It gives great benefits, especially with complex and labor-intensive calculations.
We can guess what we will understand in this lesson power levels with natural indicators and zero. The levels of rationality and their power will be discussed in lessons for 8th grade.
The step with a natural display is a number of important authorities who allow you to feel the calculations in the butts with the steps.
Power #1
Additional steps
Remember!
With multiple steps with the same bases, the base is lost without changes, and the indicators of the steps are added up.
a m · a n = a m + n, where “a” is a number, and “m”, “n” is a natural number.
This power of steps is the same as that of three or more steps.
- Forgive Viraz.
b b 2 b 3 b 4 b 5 = b 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = b 15 - The taxes are at the visible step.
6 15 36 = 6 15 6 2 = 6 15 6 2 = 6 17 - The taxes are at the visible step.
(0.8) 3 · (0.8) 12 = (0.8) 3 + 12 = (0.8) 15
Important!
Restore respect to the fact that the appointed authorities only had to go through many steps however, by new bases . It’s impossible to get close to their folding.
It is not possible to replace the sum (3 3 + 3 2) with 3 5. This is understandable, because
porahuvati (3 3 + 3 2) = (27 + 9) = 36, and 3 5 = 243
Authority No. 2
Private steps
Remember!
When dividing the steps with the same bases, the base is removed without changes, and from the indicator of the divided step, the indicator of the sharer’s step is raised.
= 11 3 − 2 4 2 − 1 = 11 4 = 443 8: t = 3 4
T = 3 8 − 4
Version: t = 3 4 = 81Corying with authorities No. 1 and No. 2, you can easily sense the inversion and carry out calculations.
- butt. Forgive Viraz.
4 5m + 6 4 m + 2: 4 4m + 3 = 4 5m + 6 + m + 2: 4 4m + 3 = 4 6m + 8 − 4m − 3 = 4 2m + 5 - butt. Know the significance of the viraza, the vikorist and power level.
= = =
=2 9 + 2 2 5
= 2 11 − 5 = 2 6 = 642 11 2 5 Important!
It is worth remembering that the authorities 2 only had about half the steps with the same basics.
You cannot replace the difference (4 3 −4 2) with 4 1. It’s clear that it’s worth it (4 3 −4 2) = (64 − 16) = 48 a 4 1 = 4
Be respectful!
Power #3
Step by stepRemember!
When a step is advanced, the step is removed without change, and the step indicators are multiplied.
(a n) m = a n · m, where “a” is a number, and “m”, “n” are natural numbers.

Power 4
Steps to creationRemember!
When brought together at the feet, the creation of skins from multiples is brought together at the steps. Then the results are multiplied.
(a · b) n = a n · b n , where “a”, “b” are rational numbers; "n" is a natural number.
- butt 1.
(6 a 2 b 3 c) 2 = 6 2 a 2 2 b 3 2 c 1 2 = 36 a 4 b 6 c 2 - butt 2.
(−x 2 y) 6 = ((−1) 6 x 2 6 y 1 6) = x 12 y 6
Important!
Restore respect to the power of No. 4, as well as other levels of power, to stand in the turning order.
(a n b n) = (a b) nSo, in order to multiply the steps with new indicators, you can multiply the bases, and leave the stage indicator unchanged.
- butt. Calculate.
2 4 5 4 = (2 5) 4 = 10 4 = 10,000 - butt. Calculate.
0.5 16 2 16 = (0.5 2) 16 = 1
In larger folding butts, drops may occur if there is an increase in the need to work on the steps with different bases and different displays. In this case, it’s best to do it this way.
For example, 4 5 3 2 = 4 3 4 2 3 2 = 4 3 (4 3) 2 = 64 12 2 = 64 144 = 9216
The butt is cranked at the steps of a tenth shot.
4 21 (−0.25) 20 = 4 4 20 (−0.25) 20 = 4 (4 (−0.25)) 20 = 4 (−1) 20 = 4 1 = 4Power 5
Private level (fractions)Remember!
To display privacy in a stage, you can display several divisions and a sharer in this stage, and divide the first result into another.
(a: b) n = a n: b n, where “a”, “b” are rational numbers, b ≠ 0, n is a natural number.
- butt. Submit in front of the private steps.
(5: 3) 12 = 5 12: 3 12
We guess that you can give a fraction in private. Therefore, on the topic of reducing the fraction to steps, we begin the report on the next page.
- butt 1.
