What is the stem of the roselin for? Classification behind the transverse re-cutting of the stem
Shaping the fabric of the stem of the secondary budovi
Secondary Budova stems are typical for mono-tree and bagatore herbaceous, village dvodolny, as well as holonaceous dews. Have dvodnykh roslin pervinne budova Even more uncomfortable, and with the ear of the cambia, a secondary structure is established. Falsely, from the bookmark of the procambium, a splinter of types of secondary buds will form. As long as the procambia are distributed in wide rows of parenchyma, then the bunch of buds will form, if the stench of closeness is so angry, they will get angry in the cylinder, - the non-bead budova will be molded.
Small. 3.24. The bunchy type of budovi of the stems of dwarf dews: A - stable: 1 - epidermis; 2 - parenchyma; 3 - sclerenchy of periclicity; 4 - phloem; 5 - bundle cambium; 6 - xylem; 7 - interbeam cambium
Puchkov budov stalks to develop in such roslin, yak stables, peas, zhovtets, krip (Fig. 3.24). They have a procambial tyazlayutsya in one colo along the periphery of the central cylinder. The skin of the procambial strand transforms into a collateral bundle, which folds into the primordial phloemia and the primordial xylem. A cambium is laid between the phloem and xylem through the procambia, which forms the element of the secondary phloem and the secondary xylem. Phloem is deposited to the periphery of the organ, and xylem is deposited to the center, and the xylem is deposited more. The primary phloem and xylem are deposited on the periphery of the beam, and the second elements lie down to the cambium. The stems of dwarf wedges are characterized by the formation of open-critical collateral or bicollateral bundles (Fig. 17, div. Col. Incl.).
Differentiation is also characteristic of the stems of dvodolny roslin primary measles, to the warehouse, which includes: collenchyma (corner (fig. 18, div. count incl.) or plate part), chlorophyllon-removable parenchyma and inner ball - endoderma. Endodermi accumulate starch; also starchy pineapple the role of the stem in the geotropic reaction is important. On the cordon of primary measles in the central axial cylinder to grow periclic sclerenchy- with a succinct circle or dilenks at a viglyad on a floem above the phloem. The core of the stem is twisted and represented by parenchyma. Ino part of the heart of the wine is ruined by the empties of the empty (div. Fig. 3.24).
Non-beam budova typical for village roslin (linden) (Fig. 19, div. count incl.) and bagatiokh herbs (lion). In the cone, the build-up of the procambial heavy is angry and set up the stem cylinder, visible on the transverse view at the viglyadi of the circle. The circle of procambia is called the form of the circle of the primordial phloem, and in the middle - the circle of the primordial xylem, between which the circle of the cambium is laid. The cambies spread (parallel to the surface organ) and are called the second phloem circle, and in the middle - the second xylem circle in the age of 1:20. Non-bead budova is visible on the butt of a large tree stem of a linden tree (Fig. 3.25).
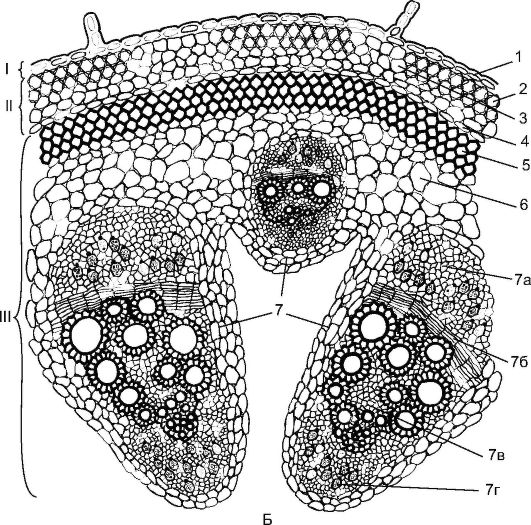
Small. 3.24.(Prodovzhennya) B - garbuz: I - crooked fabric; II - primary bark; III - central axial cylinder; 1 - epidermis; 2 - corner kollenchyma; 3 - parenchyma; 4 - endoderm; 5 - sclerenchyma; 6 - the main parenchyma; 7 - bicollateral vessel-fibrous bundle: 7а - phloem; 7b - cambium; 7c - xylem; 7d - internal phloem
The young ones flowed in the lime, scho having pretended to hang from the nirka, covered with epidermoy. All fabrics that lie before the cambium are called bark. Bark buvak is pervinnous and secondary. primordial bark It is represented by plate-like Collenchim, which grows immediately under the epidermal succinic ring, chlorophyll-bearing parenchyma and single-row starch-bearing food. At the same time, there are grains of "stolen" starch, as the roslin is not vitrized. Vvazhaєtsya, scho tsei starch take care of the fate in the growth of the growth of rivnovagi.
The central axial cylinder of a lipa is repaired with a periclic sclerene above the phloem dilens. As a result of the virtue of the cambia, the winery secondary bark(From cambium to peridermis), served with second phloem, heart swellings and parenchyma second measles. The bark is harvested from the lime, it is known to the cambium, it is especially easy to chain the hinges, if the cambia are actively moving. Previously, the bark of the lipi (liko) was vicorized for wickerwork, for making boxes, washcloths and in.
The trapezoidal phloem is divided by tricky primordial mid-grain promenades, which penetrate the tree to the heart. The phloem storehouse in lipa is not uniform. In these warehouses there is a hard bast from the woods of the fibers, and the soft bast of representations by cell tubes with cell-mates and parenchyma. Louboutin the goodness of conducting organic speeches, call it through the rik and get new balls for the action of the cambia.
Cambіy approved and the second heart of the promenade, ale the stench does not reach the heart, ruining the second village. Serve for water and water organic speeches in a radial direction. In the parenchymal cells of the heartwood exchanges, until the autumn, there are stocks of lively speeches (starch, oils), which can be added to the growing young pagones.
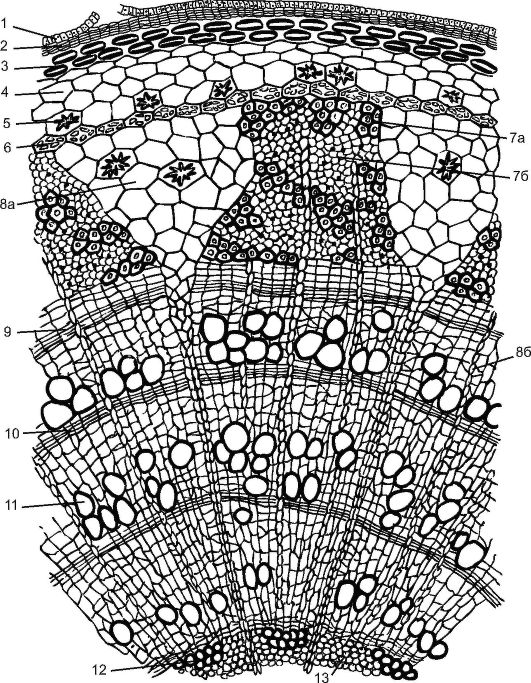
Small. 3.25. Cross-sectional razrіz of the trirіchnoi gіlki lipi: 1 - surplus epidermi; 2 - cork; 3 - plate part of the collenchim; 4 - parenchyma; 5 - friends; 6 - endoderm; 7 - phloem: 7а - hard bast, (lub'yanі fibers); 7b - soft bast - (cytovid tubes with cell-mates and lub'yan parenchyma); 8а - the first of the cores; 8b - secondary core promin; 9 - cambium; 10 - autumn tree; 11 - spring tree; 12 - pervinna xylem; 13 - parenchyma of the heart
Already for a little while before the epidermis, phellogen is laid down and the second shape is formed by the tissue - the periderm. Until the fall, with the approval of the perіderma, the children іnіdermi vіdmіyut, ale їх surplus are stored for a stretch of 2-3 years. Nasharuvannya bagatorichnyh periderm formє kirku.
A ball of xylemi, which can become a cambium, near the village roslin is much shorter, lower than a ball of phloem. The village is functional and stretches over several rocks. Children of the tree do not take part in the conducted speeches, but they do not take part in the colossal growth of the crown of the tree.
The warehouse of the tree is not uniform, it includes: tracheid(Fig. 20, div. Qty. On), trachea, derevinna parenchymaі libriform. The tree is characterized by richnikh dumplings. In early spring, if sap flow is active in winter, vines are active in the xylem form, wide-lumen and subtle provincial elements - judges and tracheids, and in the coming autumn, when the stones of the tree are processes of death, weakness and lateness Such a rank, the richest priest, or the ricnee (from one spring to іnshoi), is kindly put on the transverse vision. Behind the richest rings it is possible to see the growth of the line (div. Fig. 3.25).
Peculiarities of budova stems of dvodolnykh:
1) the growth of the stem in the trade (for the rakhunok of the activity of the cambium);
2) good differentiation of the primary bark (collenchima, chlorophyllon-borne parenchyma, starch-bearing endoderm);
3) bicollateral і bіchnі bundles only of a type іdcritical type (s cambієm);
4) vessel-fibrous bunches roztashovany on the ring or get angry (non-bunchy budova);
5) the presence of the core;
6) for village roslin, the appearance in the xylem of riches is characteristic.
Peculiarities of Budov and Dvodolny rootworms. By the covering tissue of the rootlets of dvodolnye can be epidermis, and in the bagatorial rootstocks the epidermis can be changed by the peridermis. The primary cortex is represented by the storage parenchyma and endoderm with the Casparian beaches. Moreover, the width of the primary measles is close to the width of the central cylinder. Budova central axial cylinder, vessel-fibrous bundles and growth in new may also be special, for above-ground stems.
Rounded (for example: sleepyhead)
Chotirohgranny
trigrannі
Bagatogranny (ribs) (for example: garbuz)
Krilata
stem shape
The stem, yak and root, is formed from the primordial upper meristem. At the vidminu from the root is the cone of the growth of abductions from dovkilla young countries, where leaflets develop. As in the roots of cells of the meristem they spread by mitosis and specialize in the primary permanent tissues, albeit on the basis of the roots in the stems of the green there are no clear zones of rotation. The specialization of the clientele is made more efficiently, and so it is in the roots of the clientele that the specialization is made in three of the same dilyankas.
From the periphery 1 ball klіtin transforms into periwinn I will curl the fabric; into the primordial bark; in the center of the vine is the central axial cylinder. At the stem, at the top of the root, the central cylinder is larger in size, less the primary bark. 
Pervinna on a fabric on stem epidermis, 1 ball, with stomata, with hairs. Yogo funktsiya - zakist lower structures.
primordial bark the stems are made for photosynthesis and need mechanics (to be given to the vine). Viznacha stem in the open space. Won stock from:
1) parenchyma (from 1 to deceased balls)
2) kollenchyma (from 1 to more balls). Monocotyledons develop a lot.
3) endoderm
Endoderm of the stem є 1 ball of live cells, with cellulose shells, to avenge starchy grains. The stench doesn’t є store up speech, the stench will help to open up in the open space, and that the endoderm of the stem is called starchypіkhvoyu. In addition, in the early bark of the growing roses, there can be visions in the middle of the bed, crystal-bearing cells can be developed, and the part of the stem is very plastic.
Central axis cylinder win to repair with peppercorn sclerenchy. The pericycle in the stems is reborn in the sclerenchy and chastkovo in the parenchyma. Perіtsіklіskaja sklerenchyma can be on the transverse opening at the viglyadі of the succinct circle, for in the viglyadі okremich stravіv.
Behind the pericycle, roztashovany conductive bundles, initiate collotiral; Ridko bikollotyralny otocheni by cells of the main parenchyma.
Growing of wire bunches in growing in monocotyledonous and dvodolny roselin.
- in monocotyledons, it is diffusely rosted (rosciano)
- have dvodolnykh on a stake
Also, the growth of the wire bundles is not tied to the nature of the combination of the wire bundles of the arkush and the stem
In dvodolnykh, the bunches of the leaf are brought together by the stem in their own vuzli. 
In monocotyledonous leaves, the bundles go into the central cylinder to bend and close with the stem bundles passing through 1-2 nodes. 
In dvodolny s leaves, 2-3 leaf bunches go into the stem, and in monocotyledons, at a link with parallel veins - bezl_ch.
Monocotyledonous roslin have all conductive bundles close, Tobto do not faint cambia, but in dvodolnykh vidkriti bundles, tobto є cambiy.
The comradeship of the stems of monocotyledonous grows is the same throughout the whole period, and the upper part of the stem of the monocotyledonous grows is smaller, lower in the lower part.
Stem. Morphology and function of the stem. Stem - podovzheniy in flow vishykh roslin, Service mechanic service, also the function of the provisional and support base for leaves, nirok, flowers. The stalks will bring all the parts into one system. The stalk growers will ensure the growth of the surface of the growing line by the way of its distribution, the illumination and improvement of the growth of the leaves and the generative organs. The stalk will become insensitive to the lower and lower branches of the water and to the repair in these rivers. Young pagony have the function of photosynthesis. Species of stems can be used for additional functions, for example, the accumulation and recovery of lively sprouts in bagator stems, as well as water storage in special stems, splinters of dewlap, vegetation, forgetting
The stalks of the growths are even more versatile and look for signs. For the consistency of the stem, there are: grassy or woody, empty (straw) or similar (with heart). (see the homeland of sedges), bagatogranny (see lobodi, sorrel), flattened (for example, tonkonig stisnutiy, arthroplasty). For the nature of growth and growth in space, I see the onset of the stalk: erect (mice, importantly orthotropic stems with good twisting internodes, more species of other dewlines), more vividly in the middle of the stems; zhovtets popping, ringing finger) curly (spinning around the support behind the old-fashioned arrow, or navpaki; for example, zvychanyy hop, birch polova, birch, kvassol zvychayna) to climb anyway chipky (the stalk of the fabric is covered with rosé peas, green peas) slank (the stems can be fed with a rotten mechanically fabricated fabric, which can be spread over the surface of the soil: for example, green peas, bryozoans lie, beastly spread, stelyushok) hanging (the lower part of the stem is covered with soil) thyme, zyrochnik, veronika lykarska) with more details (the stem is rotten bend Do not, even further, zblizhyuyu vuzlya, short intervuzlya and picking leaves in a rosette socket, setting a quilt arrow; for example, plantain, kulbaba, daylilies, prolisok). Species of the stem.
Species of the stem is an organ that is designated for the accumulation of spare lively words, which are necessary for growing, so that you can survive the period of calm. In addition, species of stems do not often take part in the propagation and widening of the growths. We will carry it to the whole group, the species of the stem is guilty of all the signs of the serpentine stem, so that the mother is characteristic of the new Budov, which means the apparent power of the stem from the upper point of growth against its leaves, the The visibility of a species-modified stem from a normal meadow is that it is not due to its growth above the ground, its growth is often more horizontal, and it will become a substitute for lively speeches.
The core of the main types of species-modified stems: bulba rhizome corms cibulin vus sin
Viniknennya of the first fabrics and the first anatomical budova. The anatomical budova stem of the roselin is equipped with its head functions. For a new characteristic development of mechanical and conductive fabrics of roslin. Moreover, the stem is characterized by a collapsible system of meristems - tops, bicnies and inserts, which begin to grow for a tricky hour and determine new organs.
The stalk of the wines is vinikє from the apikalnoy meristem, from which three balls of tissue are differentiated: pokrivna, yak to carry out, the main one. A collection of high-quality fabrics is represented by the so-called primordial meristem (measurement), which is stored with protoderms, procambia and basic measures. The first elements of the phloem are differentiated from the calls that are rooted on the periphery of the cells of the procambia. Pervin floema presented tonkostіnnimi nedovgovіchnimi podovzhenimi klіtinami i wear titles protofloemi and zovnіshnі klіtini її mozhut Buti predstavlenі mehanіchnimi voloknamі.Pervіchnie Elements of Xylem - traheіdi, rіdshe sudini of kіlchastimi i spіralnimi potovschennyami stіnok - vinikayut pіznіshe of vnutrіshnіh klіtin prokambіyu i viznachayutsya in tsіlomu yak protoxilemia. Prior to the її warehouse of all provincial elements, there are parenchymal cells. Later, in the middle of the protofloem and differentiation, there is a bigger type for the phloemi budov. The name of the protoxylem is formed by the metaxilema, which is stored in the tracheids or the trachea with more vigorous healthy walls.
In such a rank, for the rakhunok of the power of the procambia and the resti of the meristem of the apex of the vine, the pervinne budova stem of the rose. In monocotyledonous roslin, all procambian differentiates in the element of primary provincial fabrics. The stalks of monocotyledonous, especially grassy (grasses), in the sprinkling of the stems of dwarf dews may be more common, they are characterized in the main primary structure. metaxylem), who are usually bunched up for a rakhunok underneath clitin cambia. ... Conductive beams closed, bichni, more concentric. From the mechanical fabrics, the most developed sclerenches, the collenchims are developed at the nebatokh roslin. Secondary sweating in herbaceous monocots is mute.
Falsely from ecologic minds, in which that kind of growth is formed, there is a difference in the particularity of the structure of its organs, including the stem.
In addition, the stem is in the row of vypadkіv vikonu function of the other organs. In a wide range of changes in the structure of the stem, it is especially important and instigate to insure itself before the discharge of anomalies. Svoєrіdnim budova stems are characterized by liani. Especially richly represented by liani in the paths, de voni are most versatile and laboriously developed. Ale i v outside latitudes growth to reach the lyan. Khmіl, clematis, ivy, grapevine, peas, kvassol, glіtsinіya, birch and іn. - reference lines, not on the floor, like in the paths, but all the same in the structure of the rice stalks, the power of all the lines.
The structure of the stems of lian is characterized by rice, and the dismemberment of the wire system and the development of the parenchymal heart changes are very different. Navigate to Lian with excellent turn village stem(Grapevine) hearty exchanges are stored with parenchyma, as there is little evidence of parenchyma measles and heartwoods, and the hearty exchanges are narrower than high, to reach for great vіdstanі bridle stems, nagaduyuchi dovgі, vertically placed bridles of the stem of the strіchki, scho razdіkayut arrays of the central cylinder on the outskirts of the sector. In typical village roselin, there are some small spindles on the tangential branches of the tree, there may be a lot of short spindle-like clays. Still more dismemberment of the central cylinder of the stem appears in tropical lianas. Among the children of tropical lians, the parenchymal cells can be repaired in the small mountains of the tree of the central cylinder. As a result of the old stems of such lines, they become even more irregular and vibrating buds. Zagalom budov stalks of village lian nagaduє budov stalks deyaki grassy roslin.
In a number of dewlines, which grow in the wilderness of Africa and America, deceased boards grow even more rarely, and for a short hour, the shape and structure of the stem are attached to particular specific rice. In such roslin, the stems are fleshy, green, take on a different shape - kul, the plates are either baked with wide plate-part ribs. Such stalks represent the function of the leaf. Leaves are often even more dry and sometimes dry thorns. Roslin with meaty stems and fast leaves are called stem succulents... Until the number of їх species of prickly pears, cacti, milkweed are introduced.
Reduction of leaf blades to dry thorns leads to a significant reduction in the surface of the vapors of all dewline, which is stored in its above-ground part as a whole from a loosely shaped stem. The stem itself is transformed into an organ, attached to the accumulation of reserves of water. There is also the possibility of storing the growth of the tree in the woods during the period of time and for the vitraction during the time of lifelessness.
In buds of curved fabrics, there are large types of succulent stems, adherent to a possible decrease in the growth of water through the transpiration. At the same time, the system of wire fabrics is greatly reduced. Mechanical fabrics in the middle of the succulent stalks become unproductive and even in the middle of the day.
Klіtinniy sіk kіtin tissuein succulent stems are stored from the range of acidic acids, candies and mucous rivers. The speech is taken by the decrease in the amount of water and the growth. The tissue of the succulent stems is even more uniform and is composed of thin parenchyma, permeated with weakly calcified vertebral bundles: the vertex in the skin bundle of the trochus, all the stench of the narrow cavity and primitive structures. Weak development of the vertebral bundles in general leads to an insignificant development of the leaf, so the leaf, in its development, stimulates the establishment of the vertebral fibrous bundles of the stem. In the typical, kindly curved, succulent stems of the secondary xylem, there is little evidence of weak cambial activity, the vessel system is composed of the primary elements, which were found in the vascular meristem. Also, physiologically, and from the point of view of history, the development of a weak conductive system in the stalks of succulent growls is very bright.
Naturally, in the middle of the succulents there are no village forms, all the stench behind its structure is grass growing.
Roslin's so called sclerenchymous type It can grow in dry plants, normal leaves and stems, the system can be stored in cannabis fibrous bundles or products of evil. Sudden elements in such beams are broad, numerically and more highly organized, less in succulents. Secondary elements in the village roslin of a group of groups twist clearly, and in the stalks of grassy roslin, the lignification of the clitin of the main parenchyma is rather high in the stalks. The mechanical system is highly developed, anatomical elements and characteristics.
The stalks of the dews, which grow near the water, are the so-called water dews, with the obvious abundance of the variety of forms of water by the same backward structural familiarity: they have a well-developed system of intercellular movements and intercellulars. The intercellular spaces of the viglyadi more-mensh of the great empty ones set up a system of twisting movements, which penetrate both the heart and the bark of the stem. At the same time, the core is especially strongly rosy, which occupies a part of the outer diameter of the stem. In water dews, especially in the middle of the monocotyledonous class, there is a mechanical system of inode over the wire system. Groups of forensic anatomical elements, taken into bunches, chime in some minor changes, lots of them, which are stored from mechanical elements, which are concentrated, importantly, along the periphery of the stem, reach
It also grows as a normal type of Budov subterranean stalks, in order to display the function of stocks, - root and bulbs. Rootsevische є with a rich flow and gain the reach of a significantly greater trade, below the above-ground pagon, if the stench does not grow steep, - in the water or the middle. At the connection with the main features of the rootstock - to serve as a storehouse of spare words - parenchymatisation of yogo fabrics є naybilsh typical for rice structure. The storing tissue in typical roots is the core, which is stored from parenchymal rounded cells, thin ones, with small intercellular spaces among them. For its massivn_stuyu the core in the rootwoods wears over the іnsh fabrics. Mechanical and provincial fabrics, acting for the tightness of the core and bark, are weaker in the rootstock, lower in the above-ground pagons.
The structure of the rootstock of the yak of the bagatorny in the course of time is stored before the incessant development of the factors of the newest middle. The infusion of a number of factors can be either bezposednim or act through the correlation in the development of the organs of the growing line: for example, the steps of the development of the leaf, the coverage of the leaf ponds, the insertion of the spare speeches, are injected into the structure of the rootstock. Especially the fallowness of the budovy and rootstock is especially noticeable at the step of the development of leaves on them.
For an hour of underground growth, since there are no scales-like other leaves on the root, it seems to form even a weak conductive system, in the xylem part it is built up from the narrow narrow-cavity structures of primitive structures. For that, as the above-ground fruiting pagin with normal great leaves grows more and more, the activity of the cambium and the village grows more and more, as well as the number and growth of the judges grow, as the structure grows larger.
The peculiar morphological peculiarity of the root crop is even shorter than the middle. Mabut, the insignificance of the increase in the number of juniors is in a tight correlation due to the weak differentiation of the leaf on the rootstock.
On rootstock, in terms of its morphology, it is similar to that of an underground species - a bulb. The main idea of the root and bulb in the triviality is: the root is the bagatorny in the flow, the bulb flies in one or two rocks. Tommy in the bulb is revealed tilki ti structural rice, Yaki rootstocks may be at the first stage of the formation of their fabrics. Perevazhanya parenchyma in bulbs is more clear, less in root.
Step parenchymatizatsii tissue on the bulb nagadu tissue on the stem of the succulent growls. So itself, yak in the stalks of succulent roslin, the whole mass of tissue bulbi, behind a vignette of curvature (periderm), is a store of tissue, permeated with weakly blamed and primitive zesty bunches of the wire system. The order of the reduction of wire fabric in a normal bulb will make sure that it does not become a mechanical fabric. The fabrics, which store the bulb, are simultaneously prompted and attached to the list of only one function - the stored stock.
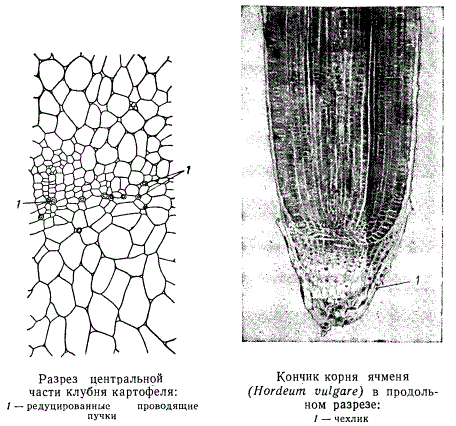
A typical butt structure of a bulb can be a bulb cartoplі. On a small image, a fragment of the transverse growth of a bulb of one of the varieties of cartopli ("Voltman"), from the central part of the second. For a visual demonstration of the fabric structure, starch, in abundance, will remember all the cells, but not images. Parenchyma of bulbi lishe in one m / s roztinuyu vuzkoy slender other clitins, which are stored in chotir'oh groups. In the skin group there are 1-3 narrow-cavity vessels, and the tissue is stored in meristem-like cells, in the middle there is a decal of cytoid tubes. The judges, which are developed by a slightly sallow structure, are primitive, and the people of them are located in the stage of obliteration and ruining.
Such fabrics, which are composed of primitive and slightly reddened rudimentary elements, are covered with a ring throughout the bulb, representing a central cylinder. Namely, the primary bark is roasted, the core is the core. In bulbs, there are only luskovidne leaves, secondary fabrics, as a result of the effectiveness of the cambia, do not establish themselves.
Yaksho vi knew the mercy, be weasel, see a fragment of the text and natisnit Ctrl + Enter.
